Ankle Instability
To ensure a stable ankle, you have three ligaments on the outside of your foot. In the case of an unstable ankle, these ligaments no longer function properly. We are happy to explain the causes of this condition and what you can do to address it! Read on for more information.
What is an unstable ankle?
An unstable ankle occurs when the ligaments are overstretched. There is a distinction between short-term and long-term ankle instability. Short-term instability is the most common and can be effectively treated with rest and the right brace. The body naturally recovers, and you should be completely pain-free within 12 weeks. If you still experience pain and discomfort after 12 weeks, it is classified as long-term ankle instability. This condition will not resolve on its own, and you will need to consult a medical specialist to determine the best treatment approach.
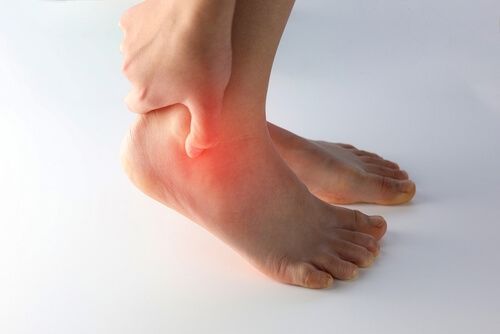
What causes ankle instability?
An unstable ankle is often caused by a sprain. When you make an incorrect movement, your ankle can twist suddenly. The foot turns inward while the ankle moves outward, stretching or even tearing the ligaments. This can be painful, and the ankle may become swollen and bruised. In most cases, the ankle heals naturally, and no further pain is experienced. However, in some cases, the ligament does not heal properly, leading to ankle instability. If this happens, further treatment is necessary.
What symptoms are associated with an unstable ankle?
Common symptoms of an unstable ankle include frequent rolling of the ankle, pain, and swelling. These symptoms often resolve on their own. Additionally, you may experience impaired coordination, loss of muscle strength, and reduced ankle stability. If your ankle frequently gives way, the risk of joint damage increases. This can eventually lead to cartilage damage, which in turn may contribute to ankle osteoarthritis in the long run.
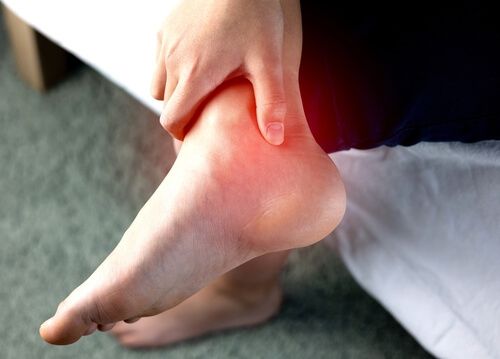
How is an unstable ankle diagnosed?
An orthopedic surgeon diagnoses ankle instability. The specialist will conduct a physical examination and inquire about your medical history. X-rays are typically taken to assess the condition of the ankle. If these do not provide sufficient insight, a CT scan or MRI scan may be performed.
What treatment options are available?
Initially, treatment aims to resolve your symptoms without surgery. Strengthening the ankle ligaments can be done using ankle taping, insoles, or an ankle brace from Podobrace. If instability persists, depending on factors such as your age, severity of symptoms, and level of physical activity, surgery may be considered.
During surgery, the ligament is reconstructed. The existing ligament is first detached, then shortened, and reattached to the bone. In some cases, if the ligament is severely damaged, a tendon may be used to create a new ligament. After surgery, a recovery period with a cast lasting six weeks is required. Physical therapy is often recommended to help restore strength to the ankle. For the first 12 weeks after surgery, you will need to be cautious with your ankle. In this phase, a brace, insole, or ankle taping from Podobrace can provide additional support.

Active Ankle T2 Sports Ankle Support
Bauerfeind MalleoLoc Ankle Support

Bauerfeind MalleoTrain S Ankle Support

Bauerfeind MalleoTrain Ankle Support
Protection level 2
Bauerfeind MalleoTrain Plus Ankle Support
Protection level 2
Bauerfeind AirLoc Ankle Support
Protection level 3
Gladiator Sports Lightweight Ankle Support with Straps

Morsa ThermoCY Lightweight Ankle Football Support
Dunimed Premium Ankle Support (Black & Beige)

- Physiotherapist
- Sports podiatrist
- Manual therapist
- Podopostural therapist
- Myofascial dry needling specialist


