Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatism in the wrist is an unpleasant condition that unfortunately cannot be cured. Fortunately, there are many treatment options available to reduce pain and make the condition more manageable.
Below, we provide additional information about the cause, symptoms, and treatments for rheumatism in the wrist. Read on to learn more:
What is rheumatism in the wrist?
Rheumatism is not a single condition, as is often assumed, but rather a collective term for more than 100 disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
When people refer to rheumatism, they often mean rheumatoid arthritis.
This condition involves chronic inflammation of the joints, leading to muscle weakness, pain, fatigue, and stiffness. In addition to rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and soft tissue rheumatism are also common.
What causes rheumatism in the wrist?
The exact cause of rheumatism is unknown. However, environmental factors such as being overweight and smoking are believed to play a role.
Heredity may also be a contributing factor. In cases of rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system not only attacks harmful invaders like viruses, but also mistakenly targets the body's own healthy tissue. When rheumatism is diagnosed in children, it is referred to as juvenile arthritis.
What symptoms can occur?
Several symptoms may be associated with rheumatism in the wrist. Below are the most common complaints:
- Pain
- Cracking or grinding sound
- Deformed joint
- Limited mobility
- Fatigue
- Swelling
How is rheumatism in the wrist diagnosed?
If you experience the above symptoms, it is important to schedule an appointment with your general practitioner. After discussing your symptoms, the doctor will perform a physical examination. An MRI scan is usually performed, and in some cases, additional tests such as a CT scan or blood work may be necessary.
What treatments are available?
Although rheumatism cannot be cured, there are a number of treatments available to help relieve the symptoms. We outline several options below. Always consult with your treating physician, who will determine the most suitable treatment for you. To manage pain, medications are commonly prescribed. There are specific rheumatism medications available, which can be taken alongside paracetamol or NSAIDs. These include, for example, diclofenac, ibuprofen, and tramadol.
Alternative treatments such as acupuncture or homeopathy may also be considered, but it is essential to discuss these with your physician and only use them in addition to your conventional treatment. In some cases, surgery may be required. This may involve cleaning the wrist joint, fusing it, or even replacing it entirely. Your doctor will advise you on which option is best for your situation.
Wearing a wrist brace is strongly recommended both with and without surgery. A wrist brace used as a rheumatism aid offers excellent support and stability, while also being very comfortable to wear.

Super Ortho - Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Wrist Support

Super Ortho Wrist Support

Bauerfeind Manuloc Wrist Support
Protection level 3
Bauerfeind ManuLoc Rhizo Wrist / Thumb Support
Protection level 3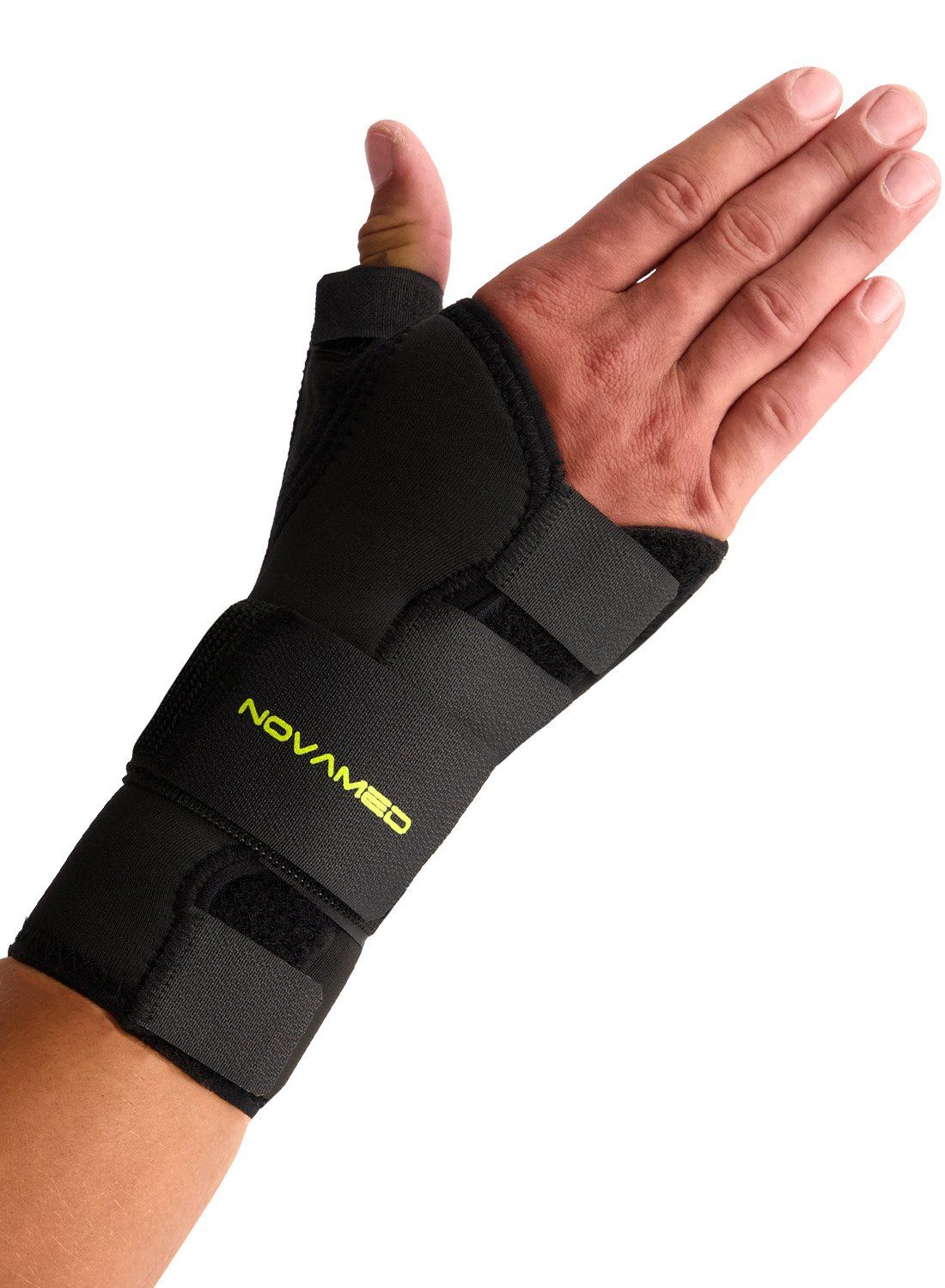
Novamed Thumb Support / Wrist Splint
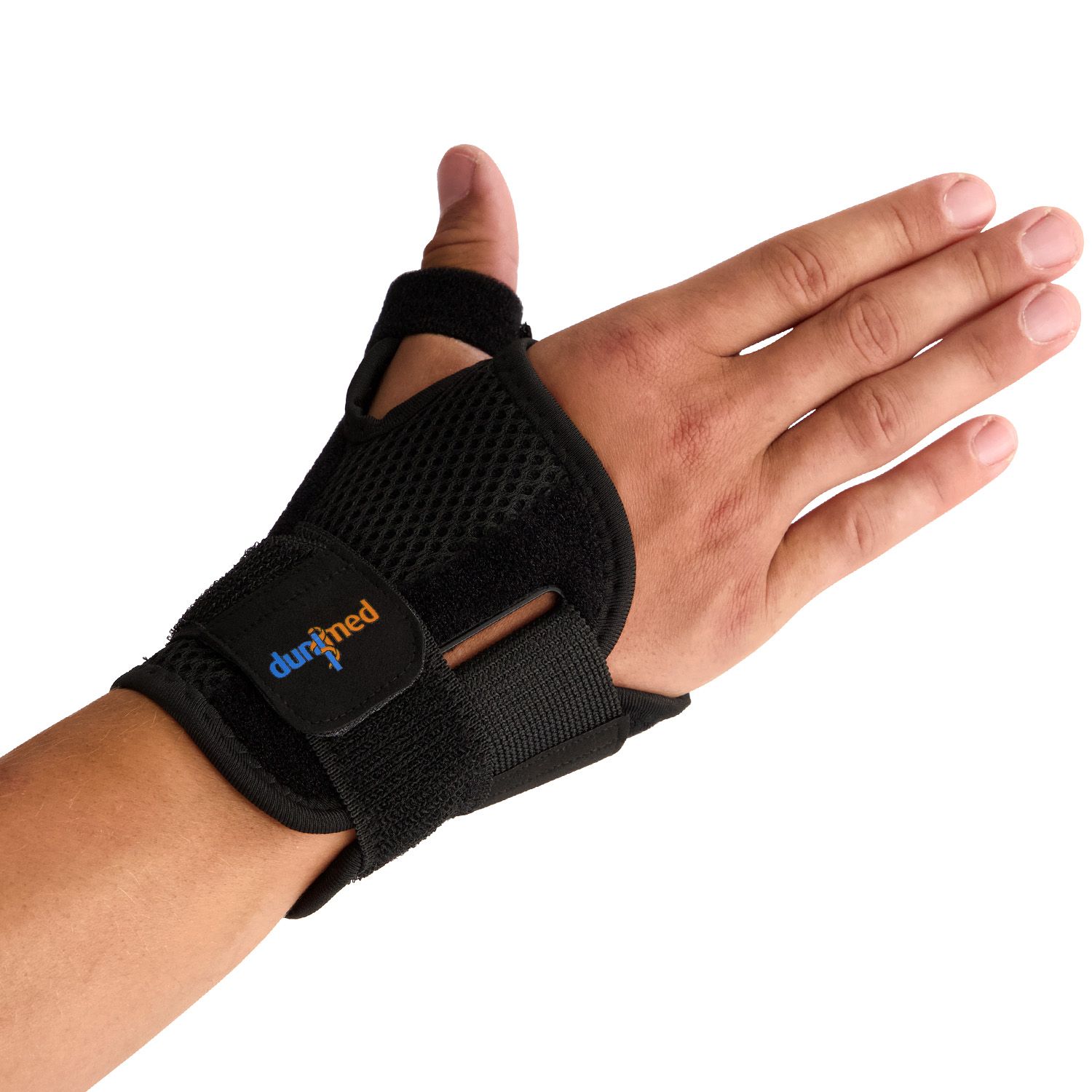
Dunimed Premium Thumb / Wrist Support
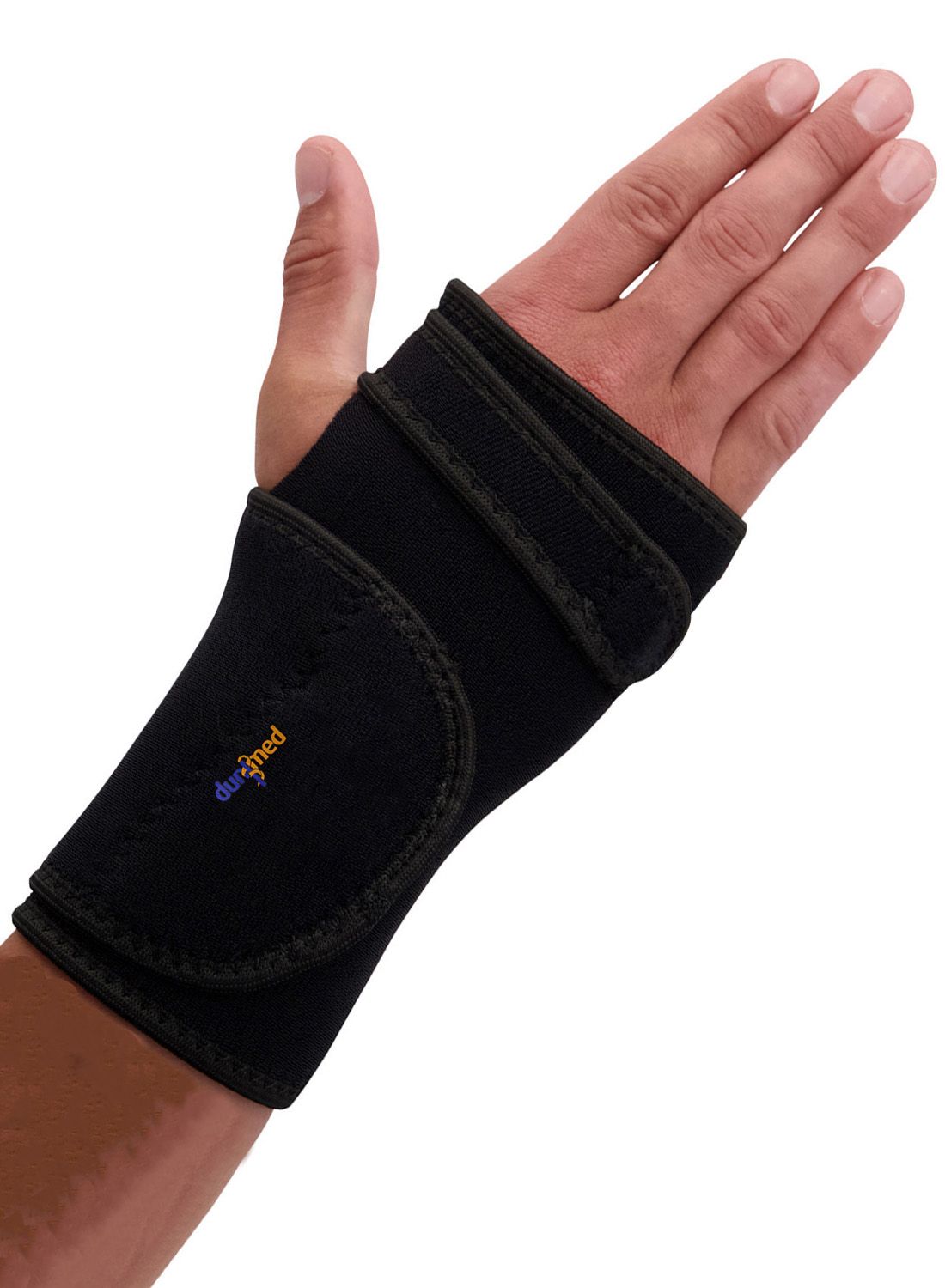
Dunimed Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Wrist Support

Dunimed Wrist Support

Dunimed Wrist Wrap

Dunimed Osteoarthritis / Rheumatoid Arthritis Gloves

Dunimed Osteoarthritis / Rheumatoid Arthritis with Anti-slip Layer
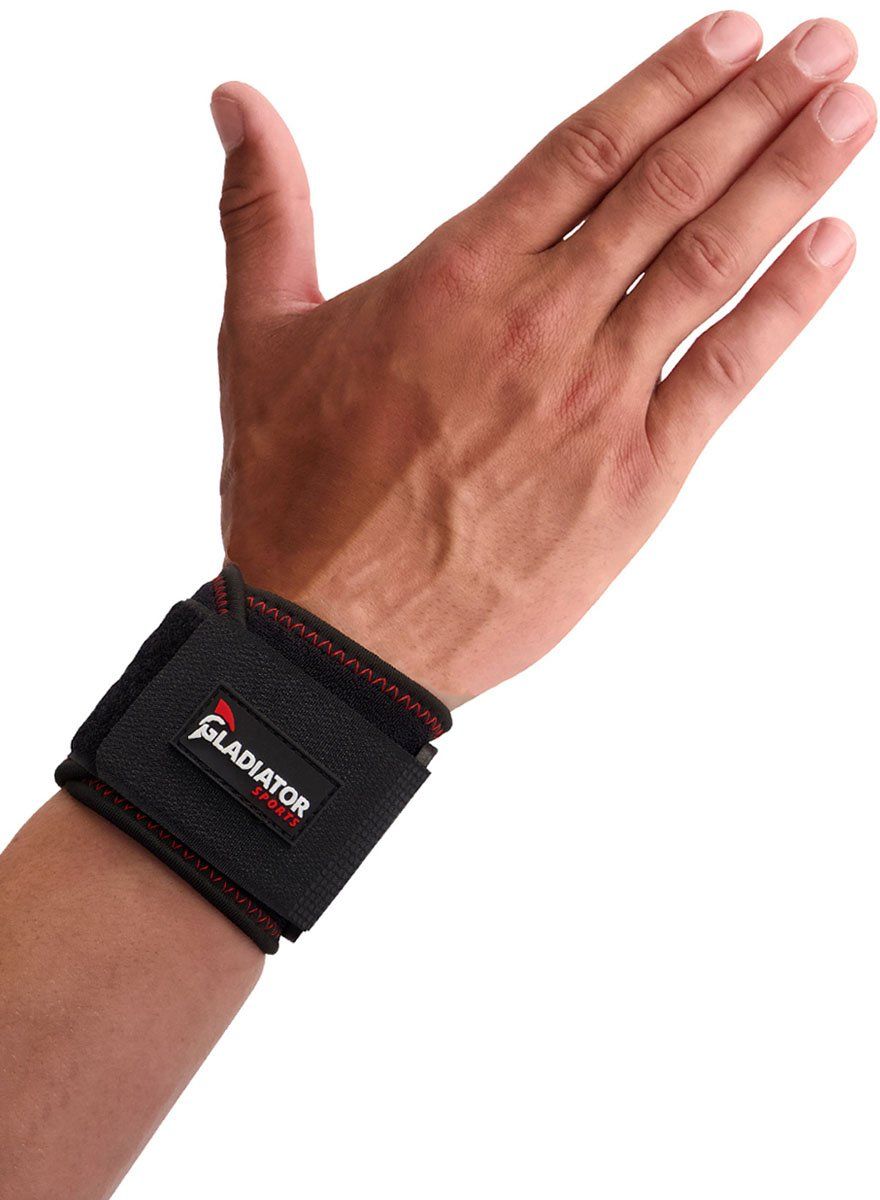

Gladiator Sports Wrist Wrap

Gladiator Sports Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Wrist Support

Gladiator Sports Thumb / Wrist Support

Gladiator Sports Wrist Support

- Physiotherapist
- Sports podiatrist
- Manual therapist
- Podopostural therapist
- Myofascial dry needling specialist


